Heart Blocks
1st Degree

Pathophysiology of 1st degree heart block
The AV node is designed to slow the propagation of signals from the atria to the ventricles, to allow time for the ventricles to contract. However if problems arise with the AV node, there can be delays in the signal propagation. These signal delays are termed "blocks".
We'll start by looking at the features of 1st degree heart block, which is usually a benign arrhythmia in itself. In 1st degree block the AV takes longer to conduct the impulses from the SAN through to the ventricles, but every beat eventually manages to conduct through to the ventricles. The result of this on the ECG is that the PR interval will be prolonged.
Causes of 1st degree block Include:
-
Increased vagal tone (common in young athletes)
-
Medications (e.g. beta blockers)
-
Inferior MIs
Adam Caar
Use this space to introduce yourself and share your professional history.
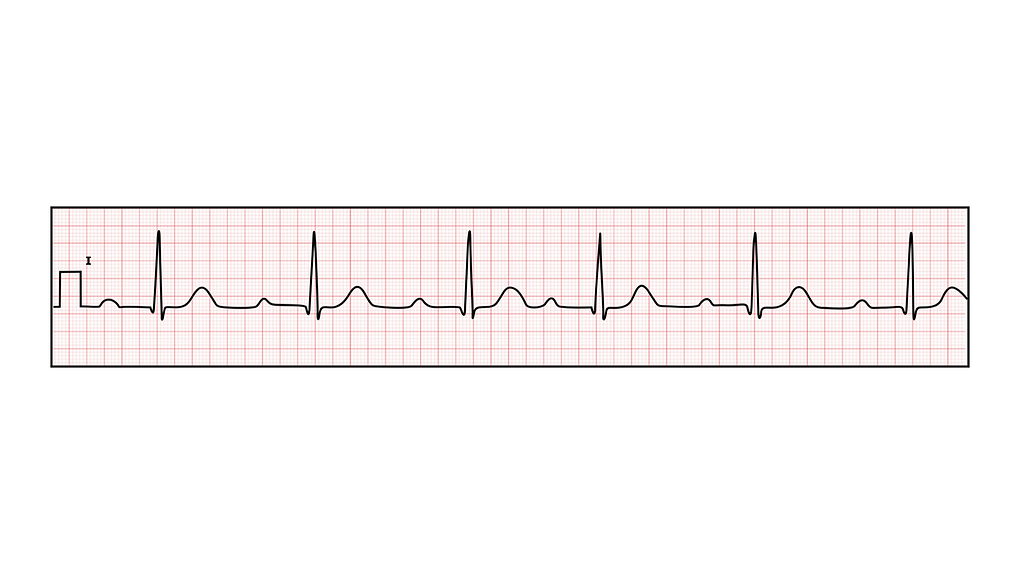

ECG findings in 1st degree heart block
ECG findings include
-
PR interval >0.2s (one large box)
-
Every P-ve should be conducted through to a QRS complex (1:1 P:QRS ratio)

